- Content
- What is influencing?
- Getting people do something, that is they benefit but they would not do it different
- Influencing style
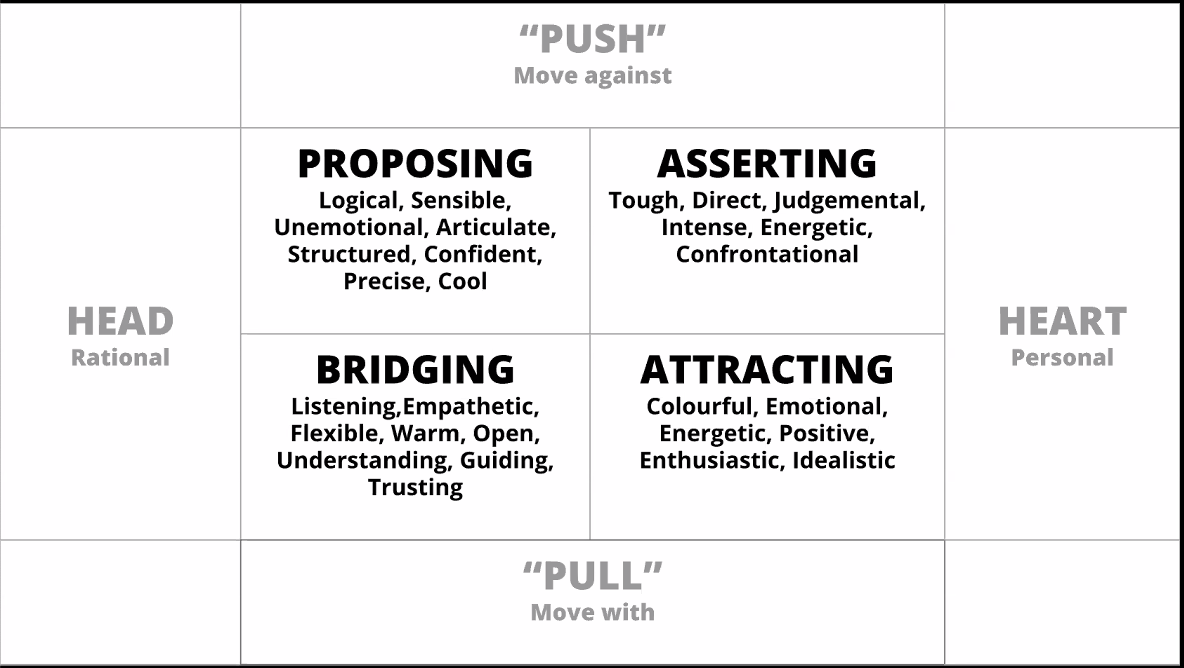
- Proposing - HEAD + PUSH
- ASSERTING - PUSH + HEART
- BRIDGING - HEAD + PULL
- ATTRACTING - HEART + PULL
- Best way to influence
- but predominantly ‘pull’ styles with a minimum if ‘push’ showedd the best results on average
- CIALDINI’S PRINCIPLES
- RECIPROCATION
- If you do something positive for some person, they feel oblige to do something for you
- CONSISTENCY
- People have the desire to appear consistent.
- If you can make them do small changes of something, then when you ask for bigger commitment of the same, they are more likely to happen
- CONSENSUS
- Social preassure, if you can convince a lot of persons that something is true, then it’s easy for them to accept
- If it’s good for others, it could be good for us
- LIKING
- People prefer to say to people that they know, or similar to us
- AUTHORITY
- People will follow the lead, for knowlegbe/respectable person.
- Setup for other people when leaving the role.
- SCARCITY
- People want more of the things, that they can have less
- Influencing with Empathy
- Empathy, is the capacity to understand what another person is experiencing.
- Collecting as much information you can, where they come from, what is the fears, their goals etc…
- The influencing “laws of gravity” → book never split the difference
- Rules:
- Fear of loss is the single biggest driver of human decision making
- Your voice will induce emotional reactions in your counterpart.
- Labeling positives reinforces them, labeling negatives diffuses them ????
- It’s not emotions that are bad for decision making, it’s negative emotions . positive emotions enhance decision making
- People remember experience based on the most intense moment & how it ended
- The desire to correct is irresistible
- Skills
- Calibrated Question
- It’s an open question
- start with what or how
- shows curiosity and replace judgements
- reinforce the other person sense of agency and control
- When to use? When you have some resistance with the client.
- example:
- Client: we don’t pair here
- How do ensure the same standards are meet throught the code?
- Client: we want all them 5 in site 5 time a week
- You can use calibrated questions, to respond to close question
- Influencing somebody without understundding their view, is very hard. Calibrated questions are fantastic for getting unstructured information.
- Don’t use why, cause it can get more acusary
- No-oriented question
- Question to give space to the other person to be able to say no.
- To want the person, to be able to say no and feel safe.
- Helps create a safe space
- gives control back to them
- Examples:
- Is now a bad time ? → I value your time
- are you in the middle of sometihng
- Would it be an issue if I walkked you throught this idea? → I value your knnowledge
- Is this a bad idea → I value your opinion
- Accusations audit
- Simply listing what somebody might be thinkking about a situation
- You put yourself inn their shoes, and try to get ahead of them
- Try to bring on nthe sun of light what they think, put their thought in the room, and dtry to work on it
- Three yeses
- If you have a yes from the counter-part
- see if you can get them to say it twice.
- Structure of a difficult conversation
- Primer Videos:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1ydwBQ1ezbbiHEPa7GhYN9evOejEjeekP?usp=sharing
- The 6 principles of persuation
https://www.influenceatwork.com/principles-of-persuasion/

